Although Microsoft SQL Server is a Windows-based database engine, you can still connect to it from a Mac using official Microsoft tools, third-party clients, or command-line utilities.
On a Mac, by far the easiest option is Azure Data Studio, Microsoft’s official tool. For advanced database management, DBeaver is a great alternative. Developers can use sqlcmd via the command line, and power users can even run SQL Server locally with Docker.
Here we’ll show you how to use each one with commands to use in Terminal.
If you’re looking for more options beyond SQL Server, you should also check out our guide to the best database software for Mac, including MS Access alternatives.
Contents
Before You Start
Before you begin, make sure you have:
- A Mac running macOS Ventura or later (Apple Silicon or Intel).
- Network access to the SQL Server instance (IP address or hostname, port
1433open). - SQL Server credentials (username + password).
- The SQL Server name/instance (for example:
192.168.1.20\SQLEXPRESSor just192.168.1.20).
Method 1: Use Azure Data Studio (Microsoft’s Official Tool)
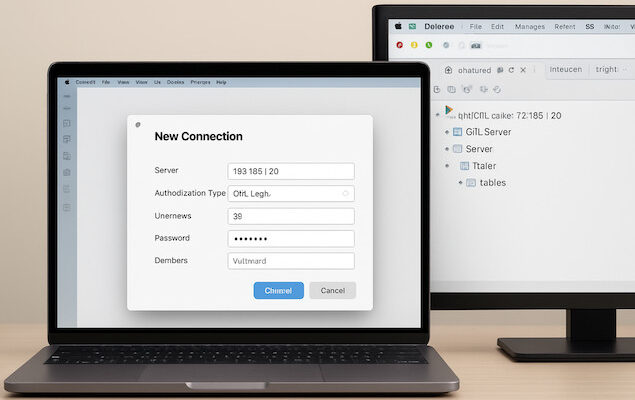
Microsoft provides Azure Data Studio (ADS), a free cross-platform SQL editor that works great on macOS.
Follow These Steps To Use It:
Download Azure Data Studio
- Go to the official Microsoft site: Azure Data Studio Download
- Download the macOS installer (Universal) for Apple Silicon & Intel.
Install
- Open the
.zipfile, drag Azure Data Studio.app into your Applications folder.
Launch Azure Data Studio
- Open it from Launchpad or Spotlight.
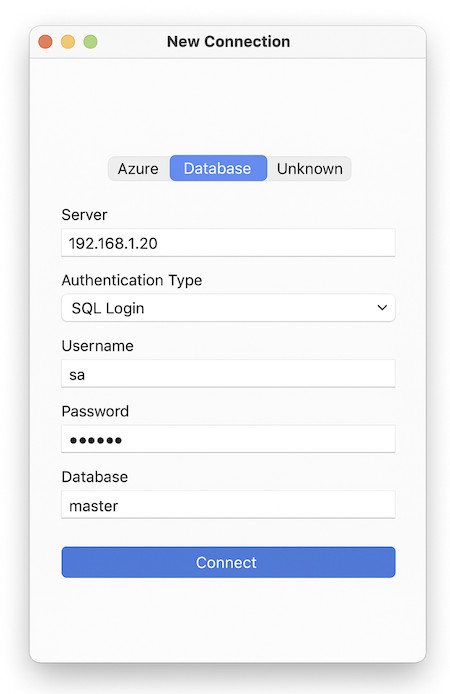
Create a Connection
- Click on “New Connection”.
- Fill in:
- Server: SQL Server IP/hostname (e.g.,
192.168.1.20). - Authentication Type: SQL Login.
- Username / Password: Your SQL credentials.
- Database: (Optional) leave blank to connect to
master.
- Server: SQL Server IP/hostname (e.g.,
Connect
- Click Connect.
- If successful, you’ll see the server in the sidebar and can start running SQL queries.
Method 2: Use DBeaver (Free Open-Source GUI)
If you want more than just SQL editing (ER diagrams, data export/import), try DBeaver.
Steps:
- Download DBeaver CE for macOS.
- Install it in Applications.
- Open DBeaver → Database > New Database Connection.
- Choose SQL Server from the list.
- Enter connection details:
- Host:
yourserver.domain.comor IP. - Port:
1433. - Database: (optional).
- Username & password.
- Host:
- Test the connection, then click Finish.
Method 3: Connect via Command Line (sqlcmd)
Microsoft also provides sqlcmd, a command-line utility for SQL Server. It’s part of the ODBC Driver + Command-Line Tools package.
Steps:
Install Homebrew (if not already installed):
/bin/bash -c “$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)”
Install Microsoft ODBC Driver for SQL Server
brew tap microsoft/mssql-release https://github.com/Microsoft/homebrew-mssql-release
brew update
ACCEPT_EULA=Y brew install msodbcsql mssql-tools
Add sqlcmd to PATH
Add this to your ~/.zshrc or ~/.bash_profile:
export PATH=”/usr/local/opt/mssql-tools/bin:$PATH”
source ~/.zshrc
Connect to SQL Server:
Run:
sqlcmd -S your_server_ip -U your_username -P your_password
Example:
sqlcmd -S 192.168.1.20 -U sa -P MyStrongPassword123
Run Queries
Inside sqlcmd, type:
SELECT @@VERSION;
GO
To exit:
EXIT
Method 4: Use Docker SQL Server on Mac (Optional for Local Testing)
If you want a local SQL Server instance on your Mac for development:
- Install Docker Desktop for Mac.
- Pull SQL Server Docker image:
docker pull mcr.microsoft.com/mssql/server:2022-latest
Run container:
docker run -e “ACCEPT_EULA=Y” -e “SA_PASSWORD=MyStrongPassword123” \
-p 1433:1433 –name sqlserver -d mcr.microsoft.com/mssql/server:2022-latest
Connect with Azure Data Studio or sqlcmd using:
- Server:
localhost - Port:
1433 - Username:
sa - Password:
MyStrongPassword123
Troubleshooting
There are some common error messages you may encounter when using some of these methods. Here’s a selection of the most common with solutions.
- “Login failed” – Double-check username/password, ensure SQL Authentication is enabled (not just Windows Auth).
- Firewall issues – Ensure port
1433is open on the SQL Server host. - Cannot resolve server name – Try using the IP address instead of the hostname.
- SSL/TLS errors – Add
TrustServerCertificate=truein connection options (DBeaver/ADS).