Each new version of macOS brings performance enhancements, feature updates, and new tools that are designed to make your Mac more efficient, secure, and fun to use.
From the early days of OS X in 2000 to the latest macOS 15 (Sequoia) in 2024, Apple has continually enhanced its operating system and hardware progressing from PowerPC Macs to Intel Macs and now Apple Silicon Macs powered by Apple’s own ARM chips.
Sometimes Apple doesn’t always please users with updates to macOS prompting some to downgrade back to an older version of macOS.
With some releases, entire models of Macs are unable to update such when macOS Sonoma dropped support for most Intel Macs (tip: there are workarounds to get around this).
And some releases are definitely more interesting than others – including the naming of them.
From the very beginning, Apple named versions of OS X after big cats but from 2013 onwards it switched to famous places in California and in 2016, switched the official name to macOS.
However, like them or loathe them, there’s no getting away from the fact that Mac users who stay updated with the latest versions usually benefit from enhanced security, better app compatibility, and interesting new features that make everyday tasks easier and improve productivity.
Here then is a trip down memory lane as we take you through a comprehensive rundown of all macOS versions since it made its debut in 2000.
Table of Contents
- OS X Public Beta Kodiak (2000)
- 1. OS X 10.0 Cheetah (2001)
- 2. OS X 10.1 Puma (2001)
- 3. OS X 10.2 Jaguar (2002)
- 4. OS X 10.3 Panther (2003)
- 5. OS X 10.4 Tiger (2005)
- 6. OS X 10.5 Leopard (2007)
- 7. OS X 10.6 Snow Leopard (2009)
- 8. OS X 10.7 Lion (2011)
- 9. OS X 10.8 Mountain Lion (2012)
- 10. OS X 10.9 Mavericks (2013)
- 11. OS X 10.10 Yosemite (2014)
- 12. OS X 10.11 El Capitan (2015)
- 13. macOS 10.12 Sierra (2016)
- 14. macOS 10.13 High Sierra (2017)
- 15. macOS 10.14 Mojave (2018)
- 16. macOS 10.15 Catalina (2019)
- 17. macOS 11 Big Sur (2020)
- 18. macOS 12 Monterey (2021)
- 19. macOS 13 Ventura (2022)
- 20. macOS 14 Sonoma (2023)
- 21. macOS 15 Sequoia (2024)
- FAQ: macOS
OS X Public Beta Kodiak (2000)

| 13 September 2000 |
Before the official launch of macOS X, Apple released a public beta version, codenamed Kodiak, in September 2000.
It was built under the guidance of Steve Jobs who had returned to Apple in order to build an operating system to compete with Microsoft Windows.
Kodiak allowed developers and early adopters to test the operating system and provide feedback before the full release.
Why it mattered: Kodiak was the first glimpse of Apple’s move to a Unix-based operating system, with its Aqua interface and new under-the-hood technologies. It cost $29.95 and provided users with a first look at what would soon become macOS X.
1. OS X 10.0 Cheetah (2001)

| 24 March 2001 |
The first official version of macOS, originally named OS X, was Cheetah.
Released in March 2001, it introduced the Aqua interface, featuring smooth graphics and the iconic “dock.”
Though visually appealing, Cheetah was known for its lack of speed, so it quickly evolved with later updates.
Why it mattered: Cheetah laid the groundwork for future macOS versions with its Unix-based structure, making it both powerful and secure.
2. OS X 10.1 Puma (2001)

| 25 September 2001 |
Later in 2001, OS X 10.1 Puma addressed performance issues and added support for more peripherals.
It was a notable improvement in system stability and speed over Cheetah.
How it went down: Early adopters saw real improvements here, but it was still a work-in-progress.
3. OS X 10.2 Jaguar (2002)

| 23 August 2002 |
Jaguar improved performance, introduced Quartz Extreme for better graphics performance, and was the first macOS to support Apple’s newly launched apps like iChat and Address Book.
Why it was useful: This is where macOS started to really come into its own as a system optimized for both casual users and professionals alike.
4. OS X 10.3 Panther (2003)
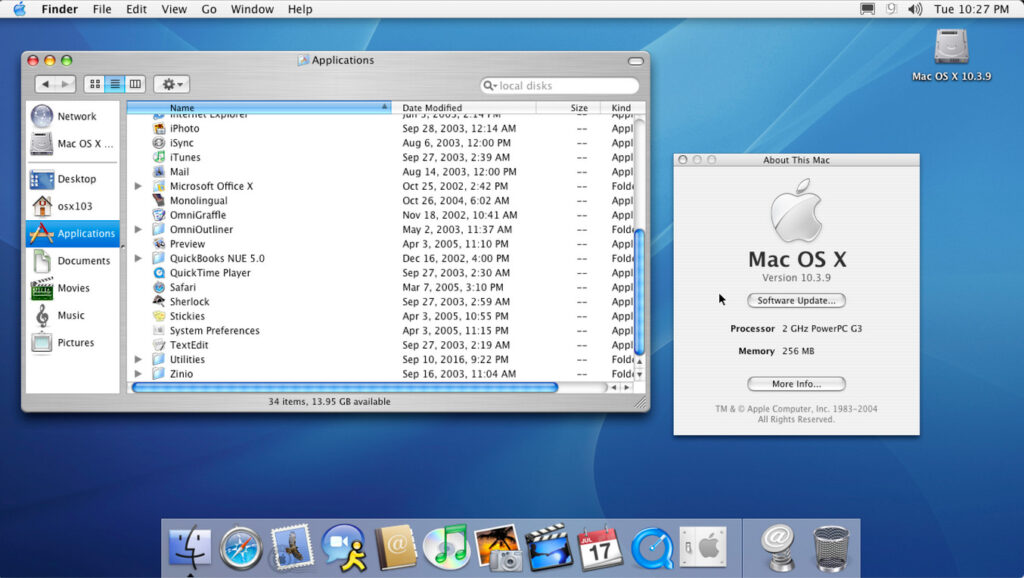
| 24 October 2003 |
Panther was faster, smoother, and featured Exposé, a new way to navigate windows quickly, still a key macOS feature today. Panther also introduced FileVault for encrypting user data.
Notable addition: FileVault was a critical feature for users who cared about security on their Macs.
5. OS X 10.4 Tiger (2005)
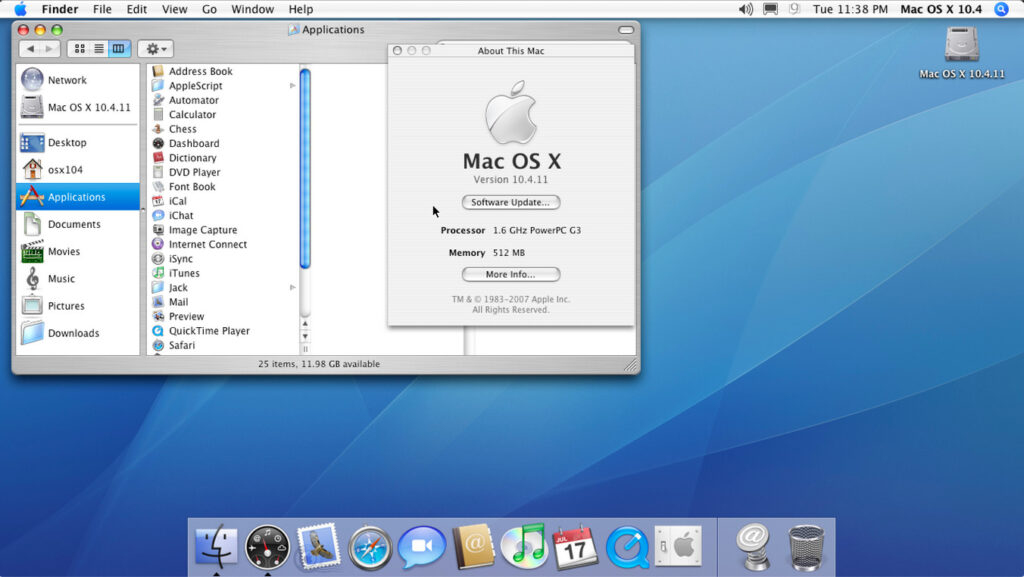
| 29 April 2005 |
Tiger brought more than 200 new features, including Spotlight for fast file searches and Dashboard for widgets.
It was also the first macOS to support Intel processors, as Apple transitioned from PowerPC chips.
Highlight: Spotlight is still an essential tool in the latest macOS versions for quickly finding documents, files, and apps.
6. OS X 10.5 Leopard (2007)

| 26 October 2007 |
Leopard introduced Time Machine for backups, and Spaces for virtual desktops, two crucial features for organization and data protection.
Best feature: Time Machine remains one of the easiest ways to back up your Mac, and it’s still in use today.
7. OS X 10.6 Snow Leopard (2009)
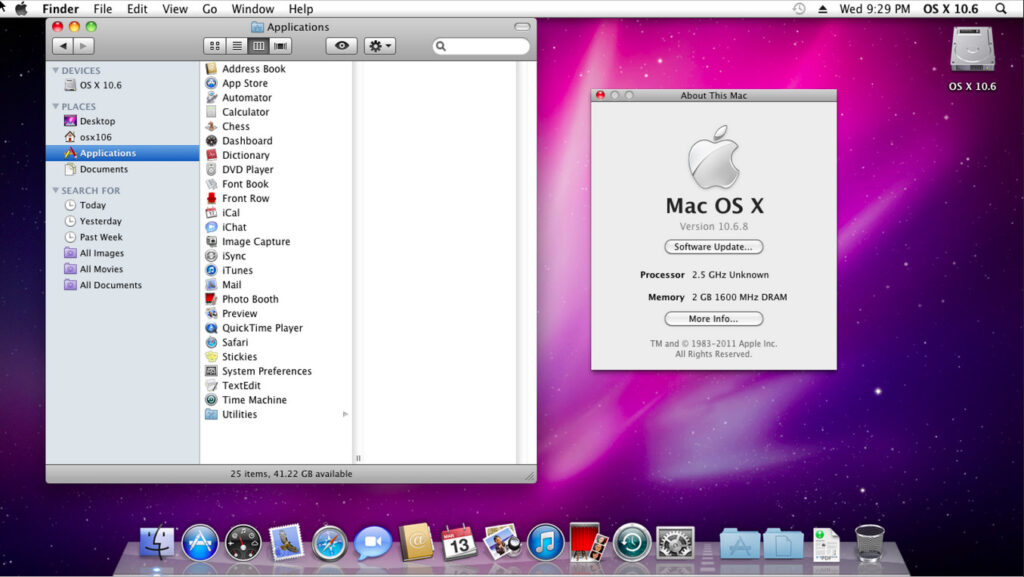
| 28 August 2009 |
Snow Leopard focused on performance enhancements and stability rather than adding new features.
It was a key version for Intel-based Macs and marked the beginning of 64-bit app support.
Why it mattered: Snow Leopard’s focus on refinement became a hallmark for future versions, setting the stage for smoother user experiences.
8. OS X 10.7 Lion (2011)

| 20 July 2011 |
Lion brought multi-touch gestures to Mac, along with the Mac App Store, Mission Control, and Launchpad for easier navigation.
Most notable for: The Mac App Store has evolved into a one-stop shop for apps, making it easier to discover and install essential tools.
9. OS X 10.8 Mountain Lion (2012)

| 25 July 2012 |
Mountain Lion continued the theme of refinement and introduced Notification Center, Game Center, and integration with iCloud.
Highlight: iCloud is now used for instant data management and syncing between Apple devices.
10. OS X 10.9 Mavericks (2013)

| 22 October 2013 |
Mavericks focused on power efficiency and introduced features like Finder Tabs, iBooks, and Maps.
Highlight: Even in 2025, using Finder Tabs can make organizing files and navigating multiple windows a lot more efficient.
11. OS X 10.10 Yosemite (2014)

| 16 October 2014 |
Yosemite introduced a completely overhauled design with flatter visuals, Continuity, and Handoff, allowing faster communication between Mac and iPhone or iPad.
Why it’s still relevant: Handoff lets you start a task on your iPhone and finish it on your Mac – especially useful in work-from-home setups.
12. OS X 10.11 El Capitan (2015)

| 30 September 2015 |
El Capitan refined the design and performance introduced in Yosemite, focusing on efficiency and introducing Split View for managing two apps side-by-side.
Highlight: Split View is excellent for multitasking, particularly when using project management software.
13. macOS 10.12 Sierra (2016)

| 20 September 2016 |
Sierra was the first version officially rebranded to “macOS” and introduced Siri for Mac.
Why it mattered: Siri’s integration helps with voice commands for productivity, something that’s only gotten better in the latest versions with the introduction of Apple Intelligence.
14. macOS 10.13 High Sierra (2017)

| 25 September 2017 |
High Sierra introduced the Apple File System (APFS), a more modern file system that improved performance and security.
Highlight: APFS is optimized for solid-state drives, giving your Mac faster boot times and app launches.
15. macOS 10.14 Mojave (2018)

| 24 September 2018 |
Mojave brought Dark Mode and Dynamic Desktop, allowing users to customize the appearance of their desktops based on the time of day.
Tip: Dark Mode can help reduce eye strain and enhance focus during late-night work sessions.
16. macOS 10.15 Catalina (2019)
| 7 October 2019 |
Catalina dropped support for 32-bit apps, introduced Sidecar for using an iPad as a second display, and added Screen Time.
Why it mattered: If you haven’t yet transitioned to 64-bit apps, Catalina forced that shift, something users must keep in mind for future macOS versions. There are still ways to run 32-bit apps on a Mac though.
17. macOS 11 Big Sur (2020)
| 12 November 2020 |
Big Sur marked the transition to macOS 11 and supported Apple’s new M1 silicon chips.
It also featured a redesigned user interface, with more vibrant colors and updated widgets.
Why it mattered: The shift to Apple Silicon meant huge performance gains for those on the latest MacBook and Mac mini models.
18. macOS 12 Monterey (2021)
| 25 October 2021 |
Monterey added Universal Control, allowing users to control multiple Apple devices with a single keyboard and mouse.
Other features included AirPlay to Mac and Focus modes.
Highlight: If you’re using multiple Apple devices, Universal Control is a game-changer for productivity.
19. macOS 13 Ventura (2022)
| 24 October 2022 |
Ventura introduced Stage Manager for window management and improvements in Spotlight search, Mail, and Safari.
Highlight: Stage Manager helps keep your desktop clutter-free by organizing windows into a single view, perfect for multitaskers.
20. macOS 14 Sonoma (2023)
| 26 September 2023 |
Sonoma focused on gaming features, adding Game Mode and improving graphics performance on Apple Silicon Macs.
Reasons to upgrade: If you’re into gaming on your Mac, Sonoma optimizes your Mac for better performance, especially when paired with the latest M-series chips.
21. macOS 15 Sequoia (2024)
| 16 September 2024 |
The latest release of macOS, which came out in 2024, builds on the success of Apple Silicon, adding AI-powered features such as Apple Intelligence, to improve user productivity, real-time collaboration tools, and deeper integration with iOS.
Highlight: AI is now embedded in every corner of macOS, from enhancing security to improving work processes with voice commands.
FAQ: macOS
What is macOS?
macOS is Apple’s proprietary operating system for Mac computers. Initially known as Mac OS X and later OS X, the name changed to macOS in 2016 to align with Apple’s other operating systems like iOS and watchOS.
Why are the names of macOS so weird?
Apple initially named OS X after big cats but in 2013, switched to naming them after places in California (where Apple is based). Internally however, Apple uses types of wine and apples to refer to versions of macOS while they are in development.
How often are macOS updates released?
Major macOS updates are typically released annually, introducing new features, performance improvements, and security enhancements.
How can I check which version of macOS I’m using?
Go to the Apple menu > About This Mac. The version number is listed under the macOS name.

Are older macOS versions still supported?
Apple typically supports the three most recent macOS versions with security updates.
Can I upgrade directly to the latest macOS?
If your Mac is compatible, you can upgrade directly via System Settings > Software Update. You don’t have to upgrade to versions of macOS in the order they were released.
How many versions of macOS have there been?
There have been 16 versions of macOS, counting from the initial public beta (Kodiak) to the latest version, Sequoia (15).
Which versions of macOS were the most important?
Here are some of the most notable and important macOS versions and why they stand out:
- Mac OS X Cheetah (10.0): Marked the official debut of the macOS lineage, introducing the Aqua interface and modern Unix-based underpinnings.
- Mac OS X Tiger (10.4): Introduced groundbreaking features like Spotlight search, Dashboard widgets, and better 64-bit support.
- Mac OS X Snow Leopard (10.6): Focused on performance and optimization, becoming one of the most stable and popular releases.
- Mac OS X Lion (10.7): Brought major user experience changes with Launchpad, Mission Control, and Auto Save, starting the transition toward a more iOS-like experience.
- OS X Mavericks (10.9): Was the first free macOS update, focusing on energy efficiency and productivity with apps like Maps and iBooks.
- macOS Sierra (10.12): Introduced Siri to the Mac, alongside features like optimized storage and Apple Pay integration.
- macOS Big Sur (11): Marked the transition to Apple Silicon with a redesigned UI and modernized architecture.
- macOS Sonoma (14): Enhanced interactivity with widgets and improved gaming performance, reflecting Apple’s increasing focus on user engagement and productivity.
- macOS Sequoia (15): Introduced Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the form of Apple Intelligence to macOS for the first time along with iPhone mirroring.
Can a Mac be too old to update?
Yes, Apple sets hardware compatibility limits for each macOS release. Older Macs may not meet the requirements for newer versions due to hardware limitations. For example, a Mac that cannot run the required processor, memory, or graphics standards won’t be able to install the latest macOS. macOS Sonoma for example was only compatible with Apple Silicon Macs and dropped support for most Intel Macs.
What’s the most common version of macOS currently used worldwide?
At the time of writing in January 2025, macOS 15.2 is the most commonly used version worldwide, with a market share of 36.95% at the end of 2024. This reflects a trend where users adopt the latest updates, as macOS 15.1 previously held the top spot with 52.66% in November 2024. These figures are according to Telemetrydeck.
How do I get older versions of macOS?
To get older versions of macOS, you can use the following methods:
- Mac App Store: If you’ve previously downloaded an older version, it might still be available in your App Store purchase history.
- Apple’s Support Website: Apple offers direct download links for older macOS versions like Mojave, High Sierra, and Catalina on its support page. You’ll need to create a bootable USB drive to install them on your Mac.
- Internet Recovery Mode: Restart your Mac and press Shift-Option-Command-R during startup. This re-installs the version of macOS that originally came with your Mac or the closest available version.
- Time Machine Backup: If you’ve created backups of your Mac, you can restore your system to a previous macOS version using Time Machine.